Maintaining Functional and Cellular Health

You want real answers to support your Functional and Cellular Health at any age. Science shows that your cells play a crucial role in your overall health. Your cells influence aging, energy levels, and how you feel daily. Studies reveal that 74% of deaths worldwide result from chronic diseases, which are closely linked to poor cellular function.
By making simple changes in your daily nutrition and lifestyle, you can enhance your Functional and Cellular Health. These research-backed nutrition tips help you take small steps toward better health every day.
Key Takeaways
Eat lots of whole foods. Choose fruits, vegetables, and leafy greens. These foods give your cells important nutrients. They help protect your cells from harm.
Exercise often to stay active. This helps your mitochondria work better. It helps your cells fix themselves. You will feel more energy.
Sleep well every night. Good sleep helps your body heal. It lowers stress. It helps your immune system work better.
Handle stress with mindfulness or meditation. You can also try gentle movement. These things protect your cells. They help slow down aging.
Eat less sugar and fewer processed foods. Drink enough water every day. Stay away from toxins. This keeps your cells healthy. It lowers your chance of getting chronic diseases.
Nutrition for Cellular Health
Whole Foods & Plants
You can help your cells by eating whole foods and plants every day. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds give your cells what they need. People who eat these foods have healthier cells and feel better. This kind of eating lowers your risk for diabetes and heart disease. It also helps with other long-term health problems. The fiber in these foods is good for your gut. It can lower swelling and help your immune system. Plants have special things called phytochemicals. These include carotenoids and flavonoids. They act like shields and protect your cells from harm. Try to fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables at each meal.
Leafy Greens & Micronutrients
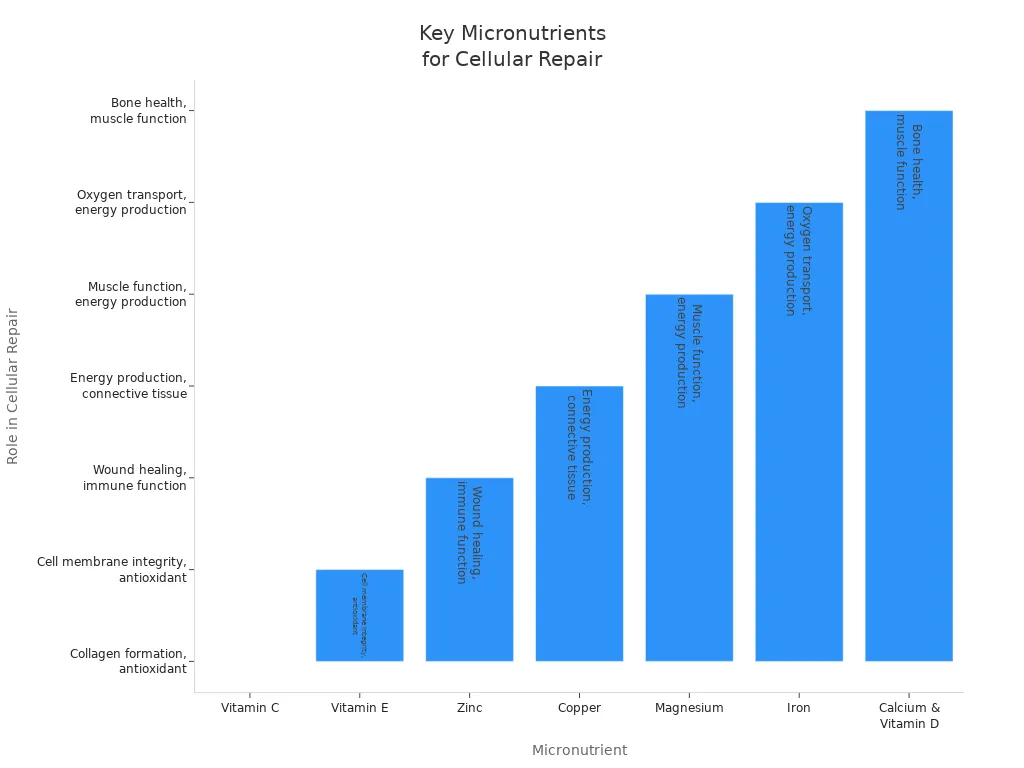
Leafy greens are great for your cells. They have lots of micronutrients that help your body fix and grow. Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard give you vitamins and minerals. These help your body heal and stay strong. Here is a table that shows some important micronutrients in leafy greens and how they help your cells:
| Micronutrient | Role in Cellular Repair and Function | Food Sources in Leafy Greens and Plant-Based Diets |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Helps make collagen for joints and skin; acts as an antioxidant and supports your immune system | Broccoli, bell peppers, citrus fruits, strawberries |
| Vitamin E | Protects cells from damage and keeps cell membranes healthy | Spinach, nuts, seeds, vegetable oils |
| Zinc | Needed for wound healing and immune health | Spinach, kale, Swiss chard, legumes, nuts, seeds |
| Copper | Supports energy production and tissue formation | Nuts, seeds, quinoa, mushrooms |
| Magnesium | Helps muscles work and makes energy | Spinach, kale, legumes, nuts, seeds, whole grains |
| Iron | Carries oxygen and helps make energy | Spinach, kale, lentils, beans, tofu, tempeh |
| Calcium & Vitamin D | Keeps bones and muscles strong | Collard greens, kale, soybeans, tofu, calcium-fortified plant milks |
Eating many kinds of leafy greens gives your body what it needs. This helps your cells and keeps you healthy as you get older.
Antioxidants & Mitochondria
Mitochondria are like tiny power plants in your cells. They turn food into energy so you can move and think. Antioxidants keep your mitochondria safe from harm. Things like stress and pollution can hurt them. Some antioxidants, like MitoQ and SS-31, help mitochondria work better. They lower stress in your cells and give you more energy. Eating fruits and vegetables gives you natural antioxidants. This helps your mitochondria and makes you feel good every day.
Hydration
Water is very important for your cells. Drinking enough water keeps your cells full and working right. If you do not drink enough, your cells shrink and cannot do their jobs. Water helps move nutrients, control your body’s temperature, and get rid of waste. Women should try to drink about 2.7 liters (91 ounces) of water each day. Men should try for 3.7 liters (125 ounces). Some of this water comes from foods like fruits and vegetables. To check if you are drinking enough, look for light-colored pee and drink so you are not thirsty. Drinking water is an easy way to help your cells and mitochondria.
Healthy Fats & Membranes
Healthy fats are needed for your cell membranes. These membranes protect your cells and help them talk to each other. Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids keep membranes strong and bendy. They help your cells send messages and fight swelling. Omega-3s are in walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds. They are good for your brain and mitochondria. Diets with healthy fats, like the Mediterranean diet, help your cells and lower swelling. Stay away from unhealthy fats like trans fats. These can make membranes stiff and hurt your cells. Eating the right fats is important for your cells.
Protein for Repair
Protein is very important for fixing your cells. When you exercise or get hurt, your body uses protein to rebuild. Eating enough protein helps your cells heal and keeps your immune system strong. After exercise, protein helps your mitochondria make more energy. It also helps your muscles grow. Older people or those healing from injuries need more protein. Try to eat plant-based proteins like beans, lentils, tofu, and tempeh for healthy cells.
Protein after exercise helps your muscles heal and grow.
It helps your mitochondria make energy.
Protein helps your immune system and lessens muscle pain.
Older people and those healing need more protein for repair.
Limit Sugar & Processed Foods
Too much sugar and processed food can hurt your cells. Eating a lot of sugar makes you age faster and can cause diabetes and heart disease. These foods can make the ends of your DNA, called telomeres, shorter. This means your cells get old faster. Processed foods have things added that can upset your gut and cause swelling. High sugar diets can also hurt your brain and mitochondria. This can lead to memory and mood problems. To help your cells, eat whole foods and try not to eat too many sugary snacks or processed meals.
High sugar and processed foods make your cells age faster.
They can cause swelling and hurt your mitochondria.
These foods upset your gut and can cause health problems.
Tip: Fill your plate with colorful fruits and vegetables. Drink plenty of water. Choose healthy fats and proteins. These easy tips will help your mitochondria and keep your cells healthy for life.
Lifestyle for Functional and Cellular Health

What you do every day affects your health. Healthy habits help your mitochondria work better and keep you feeling good. Simple changes can help you live longer and keep your cells strong.
Regular Exercise
You do not have to be an athlete to get exercise benefits. Moving your body helps your mitochondria and keeps your cells healthy. Experts say you should get at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. If you want more benefits, try for 450–750 minutes a week. Walking fast, riding a bike slowly, jogging, or biking quickly all count. Even moving for 1–2 minutes three times a day helps lower your risk of dying early.
Exercise does more than make you feel happy. It helps your cells fix themselves and keeps your mitochondria working well. When you move, your body builds new mitochondria and removes old ones. This gives you more energy and helps your muscles heal. Exercise also keeps reactive oxygen species balanced, which protects your cells. Moving often lowers your risk of long-term diseases and helps you live longer.
Exercise helps your mitochondria stay healthy and make new ones.
Physical activity gives your cells more energy by making more ATP.
Movement helps repair muscle and heart cells through autophagy.
Exercise protects against problems with mitochondria and oxidative stress as you age.
Start with small steps. Try walking after eating or stretch for a few minutes each day. Every bit of movement helps your cells and helps you live longer.
Quality Sleep
Getting enough sleep is very important for your cells. Sleep lets your body fix itself and get ready for the next day. During deep sleep, your body makes growth hormone and new proteins. This helps your muscles heal and supports your immune system. REM sleep helps your brain cells and clears out waste.
When you sleep well, your cells fix DNA and fight stress. Not sleeping enough can cause more swelling, higher stress hormones, and faster aging of your cells. Your gut health also depends on sleep, which helps your body repair.
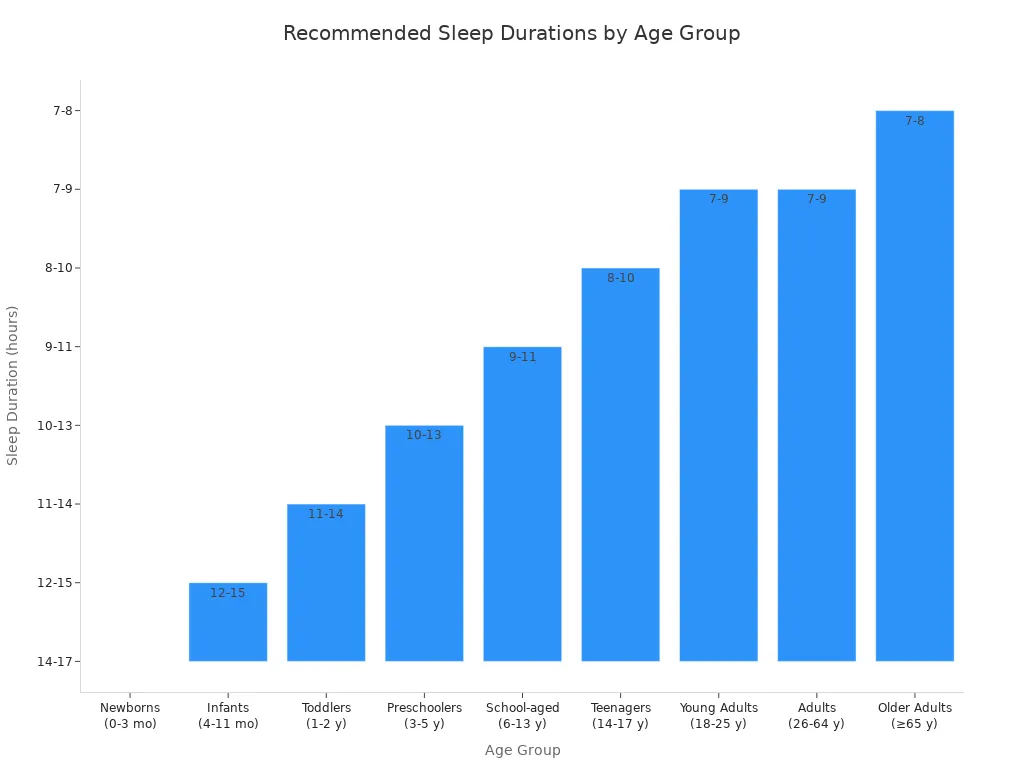
Here’s a table showing how much sleep people need at different ages:
| Age Group | Recommended Sleep Duration (hours) | May Be Appropriate (hours) | Not Recommended (hours) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Newborns (0-3 mo) | 14 to 17 | 11 to 13, 18 to 19 | Less than 11, More than 19 |
| Infants (4-11 mo) | 12 to 15 | 10 to 11, 16 to 18 | Less than 10, More than 18 |
| Toddlers (1-2 y) | 11 to 14 | 9 to 10, 15 to 16 | Less than 9, More than 16 |
| Preschoolers (3-5 y) | 10 to 13 | 8 to 9, 14 | Less than 8, More than 14 |
| School-aged (6-13 y) | 9 to 11 | 7 to 8, 12 | Less than 7, More than 12 |
| Teenagers (14-17 y) | 8 to 10 | 7, 11 | Less than 7, More than 11 |
| Young Adults (18-25 y) | 7 to 9 | 6, 10 to 11 | Less than 6, More than 11 |
| Adults (26-64 y) | 7 to 9 | 6, 10 | Less than 6, More than 10 |
| Older Adults (≥65 y) | 7 to 8 | 5 to 6, 9 | Less than 5, More than 9 |
Tip: Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day. Make your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet. These easy steps help your cells repair and support your mitochondria.
Stress Management
Stress can hurt your cells and make you age faster. When you are stressed for a long time, your body makes more stress hormones. This makes your telomeres shorter, so your cells get older faster. Long-term stress also causes more swelling and hurts your mitochondria.
You can fight stress with simple things. Mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises lower stress hormones and help your cells heal. These activities also help you sleep better and feel happier. When you manage stress, you protect your cells and help yourself live longer.
Mindfulness and meditation lower swelling and oxidative stress.
Yoga and tai chi help balance stress hormones and repair cells.
Good sleep and regular exercise also lower stress and protect your mitochondria.
Try taking deep breaths or spending time outside. Small changes can really help your cells.
Social Connections
Having friends and family helps you live longer and keeps your cells healthy. People with strong social ties have over 50% higher survival rates. Being lonely or alone can raise your risk of heart disease, stroke, and dementia. This happens because being alone causes more swelling and stress, which hurts your cells and mitochondria.
Social bonds lower stress and help your body make oxytocin. This hormone helps your brain and helps your cells heal. Spending time with others makes you feel better and helps you live longer.
Being alone causes more swelling and makes your cells age faster.
Loneliness raises blood pressure and stress hormones, which hurts your heart and brain.
Support from others helps you keep healthy habits and get better if you are sick.
You can make friends by joining clubs, helping others, or talking to loved ones. Even small talks help your cells.
Avoid Toxins
Toxins in the environment can hurt your cells and mitochondria. Chemicals like BPA, phthalates, and heavy metals cause oxidative stress and swelling. These toxins make your cells age faster and raise your risk of disease. Air pollution, pesticides, and mold also hurt your heart, brain, and reproductive health.
You can lower your risk by using natural cleaning products, eating organic foods, and staying away from plastics. Testing for toxins and using detox steps can help protect your health.
Chemicals like BPA and phthalates are linked to cancer and reproductive problems.
Heavy metals like lead and mercury hurt your heart and mitochondria.
Air pollution raises the risk of heart disease and makes your cells age faster.
Note: Eating well, moving often, and managing stress help your body fight toxins and keep your cells healthy.
Your choices matter. When you move, sleep well, handle stress, connect with others, and avoid toxins, you help your cells stay strong. These habits help your mitochondria, make you feel better, and help you live longer. Small changes add up and help prevent disease and keep you healthy.
Advanced Ways to Improve Cellular Health
Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting can help your cells stay healthy. This means you take breaks from eating. When you do not eat for a while, your mitochondria can rest and fix themselves. Fasting helps your cells clean out old or broken parts. This keeps your body strong and young. Short fasts, like 16 to 24 hours, help your liver, muscles, and brain. Longer fasts can help even more by cleaning mitochondria and helping your cells get nutrients. Here is a table that shows what happens when you fast:
| Aspect | What Happens in Your Body |
|---|---|
| Autophagy Activation | Fasting lowers insulin and turns on AMPK. This starts autophagy and helps fix your cells. |
| Cellular Rejuvenation | Fasting turns on genes that help cells renew. It also lowers signs of aging. |
| Health Benefits | You get better blood sugar, less swelling, better cholesterol, and stronger mitochondria. |
You do not have to fast for many days. Even skipping breakfast or eating in an 8-hour window can help your cells and help you live longer.
Supplements
Supplements can help your cells get the nutrition they need. They also help your mitochondria work better. Some good supplements for health are creatine, B vitamins, NMN, curcumin, magnesium, CoQ10, and vitamin C. These help your cells make energy, fix DNA, and fight stress. Here is a table with some top supplements:
| Supplement | How It Helps Your Cells | Dosage/Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Creatine | Gives you more energy and helps fix cells | 3–5 g daily |
| NMN | Helps mitochondria and insulin work better | 250–500 mg daily |
| CoQ10 | Protects mitochondria and fights damage | 60–500 mg daily |
| Magnesium | Fixes DNA and helps autophagy | Not specified |
| Curcumin | Lowers swelling and helps fix DNA | Not specified |
Ask your doctor before you start new supplements. The right mix can help your cells and help you live longer.
Gut Health
Your gut has trillions of tiny bacteria. These bacteria help your cells get the nutrition they need. A healthy gut keeps you from getting sick. It helps you take in nutrients and keeps your immune system strong. If your gut bacteria are not balanced, you might get sick or have swelling. Eating foods with fiber, fruits, and vegetables feeds good bacteria. Stay away from processed foods to keep your gut and mitochondria healthy.
Tip: Try eating fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, or sauerkraut. These foods help your gut bacteria and support your cells.
Personalized Nutrition
Everyone’s body is different. Personalized nutrition uses your genes, habits, and health data to make a plan just for you. New technology lets you track your food and cell health with apps and sensors. Personalized plans can lower cholesterol, help mitochondria, and make it easier to keep good habits. You get advice that fits you, so it is easier to help your cells and reach your health goals.
Personalized plans use your genes and habits to help you choose.
You can get better results than with general tips.
Tracking your progress helps you stay on track and helps your cells.
You can support cellular health by combining smart nutrition, active living, and new strategies.
Eating well, moving often, and using personalized tools work together to keep your cells strong.
Small steps, like adding leafy greens or walking daily, make a big difference over time.
Studies show that steady changes help you feel better and lower your risk for disease.
Start with one or two tips today. Your future self will thank you for every step you take!
https://holisticwellnesswave.com/index.php/2025/08/21/preventing-cardiovascular-disease-essential-health-strategies/
FAQ

What is the best way to start improving my cellular health?
Start small. Add more fruits and vegetables to your meals. Drink more water. Move your body every day. These simple steps help your cells right away.
Can I boost my cellular health without supplements?
Yes! You can eat whole foods, get enough sleep, and manage stress. These habits support your cells. Supplements help, but you do not need them to see results.
How does exercise help my cells?
Exercise helps your body make new mitochondria. These are the power plants in your cells. Moving your body also helps your cells repair and gives you more energy.
Is it safe to try intermittent fasting?
Most people can try short fasts, like skipping breakfast. If you have health problems or take medicine, talk to your doctor first. Start slow and listen to your body.
Do I need to follow a strict diet for healthy cells?
No, you do not need a strict diet. Focus on eating more whole foods and less sugar. Small changes add up. You can enjoy treats sometimes and still help your cells.





